The efficiency of medical imaging systems is crucial for diagnosis and treatment and the broader management of patient data.
Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS) stand at the forefront of this technological nexus, offering more than just storage solutions. These systems encapsulate the seamless image retrieval, management, and distribution integration that supports modern medical practices.
This blog delves into the fundamental roles PACS plays within healthcare settings, highlighting how these systems safeguard vital medical images, streamline operations, enhance collaborative medical efforts, and elevate patient care standards across the board.
Join us as we explore each core function of PACS and its profound impact on medical workflows and patient outcomes.
PACS, or Picture Archiving and Communication Systems, revolutionized medical imaging by transforming how healthcare facilities store vast imaging data. At its core, PACS is designed to handle large-scale image storage efficiently. This system leverages high-capacity servers that store everything from standard X-rays and MRIs to complex CT scans, enabling instant access and management.
The technology behind these servers is robust and sophisticated, ensuring they can manage the extensive data volumes without lag or information loss. Modern PACS servers utilize advanced data compression methods to maximize storage efficiency while maintaining high image quality. They also employ redundant storage solutions to safeguard data against potential hardware failures, ensuring that medical records are always accessible when needed.
Over the years, storage solutions within PACS have evolved significantly, adapting to the changing needs of healthcare. Initially, these systems relied on ample physical storage, which was both costly and cumbersome.
Today, integrating cloud storage solutions has expanded capacity and enhanced accessibility. It allows healthcare professionals to access vital imaging data from anywhere, drastically improving the flexibility and responsiveness of medical services.
This evolution underscores PACS's pivotal role in enhancing healthcare systems' operational capabilities, ensuring they can keep pace with medical diagnostics' increasing demands.
Integrating data analytics tools into Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS) is revolutionizing how medical facilities manage and utilize imaging data. These tools enable healthcare providers to harness vast imaging data to uncover trends, assess performance metrics, and optimize operational efficiencies.
This capability enhances the diagnostic process and improves overall healthcare delivery by providing critical insights that inform clinical and administrative decisions.
Data analytics within PACS allows healthcare organizations to move beyond traditional data storage and retrieval roles, transforming raw data into strategic insights. Here’s how these tools are making a difference:
• Trend Analysis: By analyzing imaging data over time, PACS, with data analytics, can identify patterns and trends in disease prevalence, treatment outcomes, and patient demographics. This information is crucial for predicting future healthcare needs and preparing resources accordingly.
• Performance Metrics: Data analytics tools measure and report on various performance indicators, such as the speed of image retrieval, the efficiency of image processing, and the accuracy of automated diagnostics. These metrics are vital for continuous improvement and ensuring that the PACS meets the evolving needs of the healthcare facility.
• Resource Allocation: Healthcare managers can optimize resource allocation by understanding the workflow and utilization rates of different imaging modalities. For example, data insights can help schedule MRI machines more efficiently, reducing wait times and increasing patient throughput.
The analytical capabilities embedded in PACS also support clinical decision-making by providing a comprehensive view of patient histories and imaging results. Clinicians can access aggregated data that may reveal correlations between imaging findings and patient outcomes, aiding in formulating more personalized treatment plans.
Several healthcare institutions have leveraged PACS with data analytics to notable effect. For instance, an extensive hospital network implemented analytics to monitor the usage patterns of their imaging equipment and found ways to reduce unnecessary scans, resulting in cost savings and reduced patient exposure to radiation. Another example is a research facility that used PACS data analytics to study the progression of chronic diseases, which contributed to the development of more effective treatment protocols.
While the benefits are significant, integrating data analytics into PACS comes with challenges:
• Data Quality And Integrity: Ensuring the accuracy and completeness of imaging data is crucial for reliable analytics. Data quality can lead to correct insights, adversely affecting patient care.
• Privacy And Security: Handling sensitive medical data requires stringent security measures to protect against breaches and ensure compliance with regulations like HIPAA. Balancing accessibility and security is crucial in the design of these systems.
The retrieval process within PACS (Picture Archiving and Communication System) is a cornerstone of its utility, enhancing healthcare providers' ability to access patient imaging swiftly and efficiently.
PACS retrieves the data from its vast repositories—local servers or cloud storage when an image request is made. This system supports multiple imaging modalities, ensuring that MRI, CT scans, X-rays, and other forms of medical imaging are readily available.
The efficiency of PACS is particularly evident in its impact on hospital workflows. By reducing the time traditionally spent on manual retrieval from physical archives, PACS allows medical staff to access necessary images within seconds.
This rapid access is crucial not just in routine check-ups, where time efficiency leads to increased patient throughput, but most critically in emergency care settings. Here, every second counts, and quickly pulling up a patient’s historical and current images can be lifesaving, providing immediate insights for urgent decision-making.
This quick data retrieval facilitated by PACS isn't just a matter of convenience but a substantial improvement in medical care standards. It enables healthcare facilities to provide prompt, informed responses to patient needs, enhancing the effectiveness of medical interventions and patient outcomes.
This capability illustrates how PACS is more than just a technological upgrade—it is an essential component of modern medical operations that aligns with the fast-paced demands of healthcare delivery.
 - Presented by PostDICOM.jpg)
PACS (Picture Archiving and Communication System) offers advanced management tools that revolutionize how medical images are handled within healthcare settings. These tools go beyond mere storage; they empower radiologists and other medical professionals with capabilities to process, annotate, and adjust images, thereby enhancing diagnostic accuracy.
At the core of PACS's functionality is its ability to facilitate detailed image processing. This includes refining image clarity and contrast, allowing for a closer examination of intricate structures within the body.
Radiologists can apply annotations directly to the images, noting areas of concern or interest. These annotations become integral to collaborative case reviews, where multiple specialists might examine the same images from different locations, ensuring that critical information is communicated effectively.
Moreover, PACS is designed to work seamlessly with other diagnostic tools, forming an interconnected network within medical facilities. This integration ensures that imaging data is readily available across various platforms, from ultrasound to MRI, creating a unified system that supports a comprehensive approach to patient diagnostics.
Such connectivity streamlines the workflow and enhances healthcare providers' capacity to deliver high-quality care based on a holistic view of patient data.
This sophisticated management and integration capability underscores the transformative role of PACS in healthcare. It’s not just about storing images but effectively managing and utilizing them to forge more apparent paths to accurate diagnoses and informed treatment plans, ultimately advancing the standard of patient care.
PACS fundamentally changes how medical images are shared within the healthcare ecosystem. Its ability to facilitate the rapid distribution of imaging data across different departments and even between distinct healthcare facilities is a cornerstone of modern medical practices, significantly improving collaborative efforts and patient outcomes.
The system ensures that medical images are readily available where and when needed, irrespective of geographical barriers. This capability is crucial in scenarios requiring multidisciplinary consultation, where specialists from various locations analyze the same medical images in real time to make swift, informed treatment decisions.
However, broad access to sensitive data requires stringent security measures. PACS systems have advanced security protocols to safeguard patient information, complying with health information privacy laws such as HIPAA in the United States. These measures include data encryption, secure access controls, and audit trails that ensure only authorized personnel can access the data and all access instances are logged.
For instance, a health system spanning multiple states might use PACS to distribute images from a rural clinic to a specialized urban medical center, facilitating expert review and quick diagnosis that could be critical to the patient’s recovery. Another example is in emergency care, where the ability to send and retrieve images quickly can drastically cut down response times and improve the chances of successful outcomes.
These case studies illustrate how effective image distribution through PACS supports medical professionals in their daily tasks and elevates patient care across different settings. Through seamless integration and robust security, PACS remains an indispensable asset in healthcare, pushing the boundaries of what can be achieved in medical diagnostics and treatment planning.
Integrating mobile access into Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS) represents a significant leap forward in medical imaging technology. This feature allows healthcare professionals to view patient images and diagnostic reports directly from their smartphones and tablets, fundamentally transforming the delivery of patient care by enhancing accessibility and enabling rapid decision-making.
Mobile access to PACS empowers doctors, nurses, and other healthcare providers to retrieve and review medical images anytime and anywhere. This capability is particularly crucial in urgent care scenarios where time is of the essence.
For instance, in emergencies or during off-hours, when specialists may not be immediately available on-site, the ability to access relevant patient data through a mobile device quickly can speed up diagnostics and the initiation of appropriate treatments.
Modern PACS are designed with applications optimized for mobile devices, offering interfaces that maintain the integrity and detail of medical images on smaller screens. These applications often include features such as:
• Zoom And Adjust: Users can zoom in and out and adjust image parameters to view fine details, much like they would on dedicated workstations.
• Annotations And Measurements: Mobile apps allow marking up images and taking measurements directly on the touch screen, which can be saved and shared within the PACS for later review.
• Secure Access: Security is paramount, especially when accessing sensitive medical data over mobile devices. Mobile PACS applications have robust security measures, including encryption and secure login procedures, ensuring compliance with health data privacy regulations such as HIPAA.
Several healthcare institutions have reported enhancements in operational efficiency and patient outcomes due to the mobile capabilities of their PACS. For example, a regional hospital implemented mobile access to their PACS and observed a 30% reduction in starting treatment for stroke patients. This improvement was primarily due to the rapid availability of brain scans to attending neurologists, regardless of their physical location.
While the benefits are significant, there are also challenges to consider:
• Image Quality On Mobile Devices: Ensuring that the image quality on mobile devices is sufficient for accurate diagnosis is critical. Not all mobile screens offer the resolution and color accuracy of medical-grade monitors.
• Data Consumption And Network Reliability: Streaming high-quality medical images can consume substantial data. Additionally, the reliability of mobile networks can vary, potentially affecting the speed and consistency of image delivery.
In conclusion, PACS is a pillar of modern healthcare, significantly enhancing medical image management, retrieval, and distribution. From streamlining workflows to fostering collaboration across healthcare facilities, PACS is critical in ensuring that patient care is efficient and comprehensive.
By integrating seamlessly with other hospital systems like RIS and EHR, PACS enhances operational efficiencies and enriches the quality of patient diagnostics and outcomes. As technology advances, we can anticipate even more sophisticated integrations and capabilities, making PACS an even more invaluable tool in healthcare providers' arsenals.
Embracing these advancements will be critical to leveraging medical imaging technology's full potential in pursuing superior patient care and optimized healthcare delivery.
|
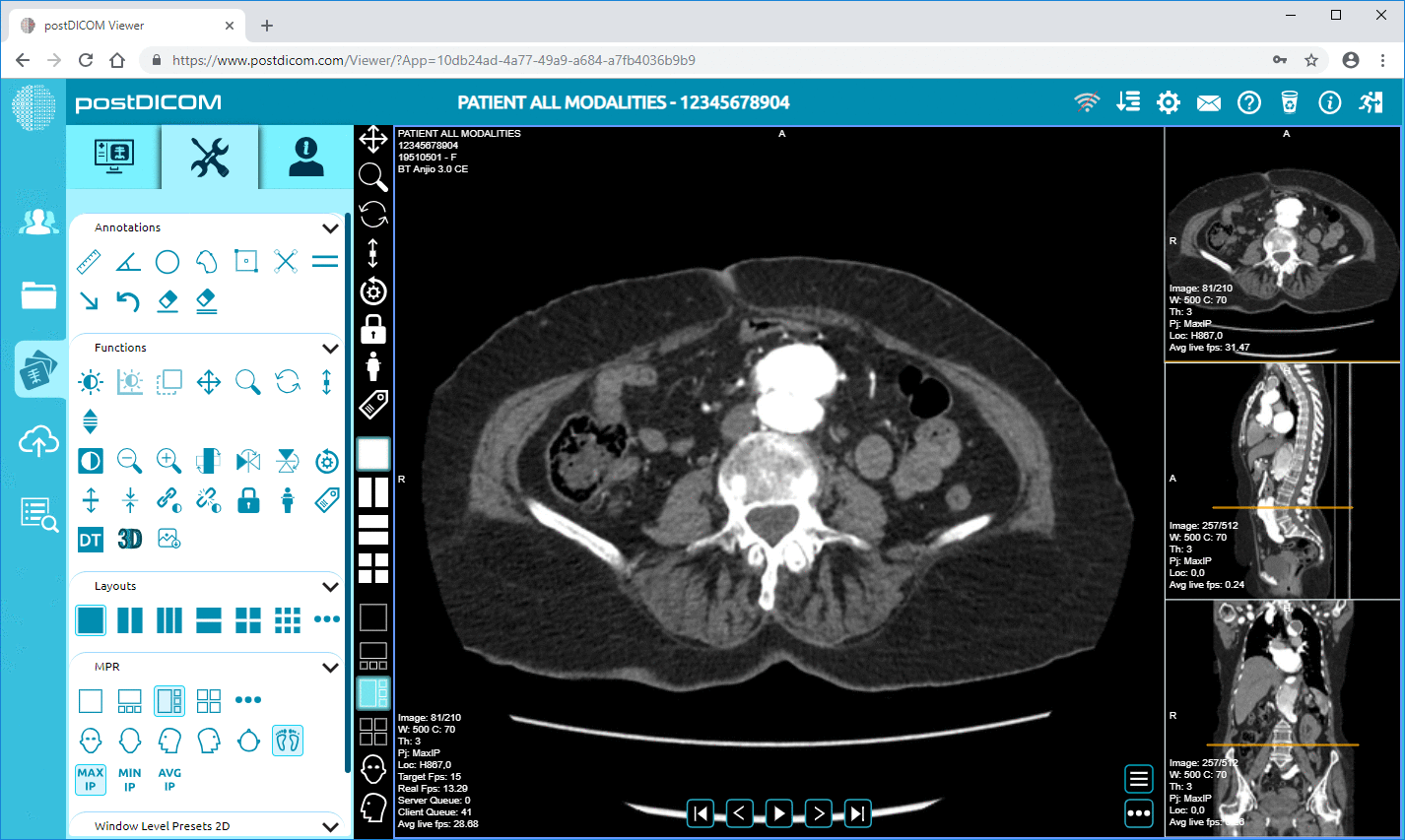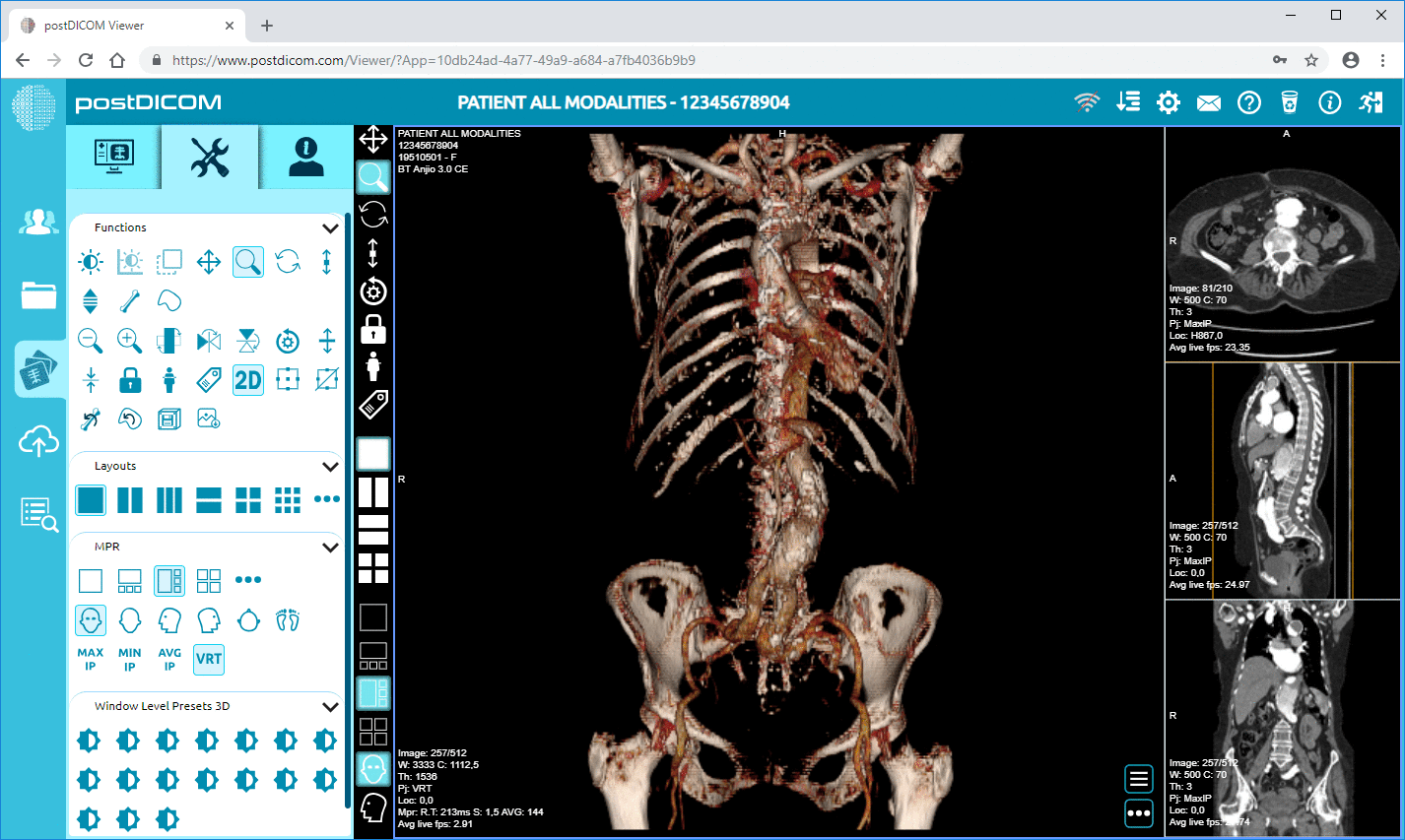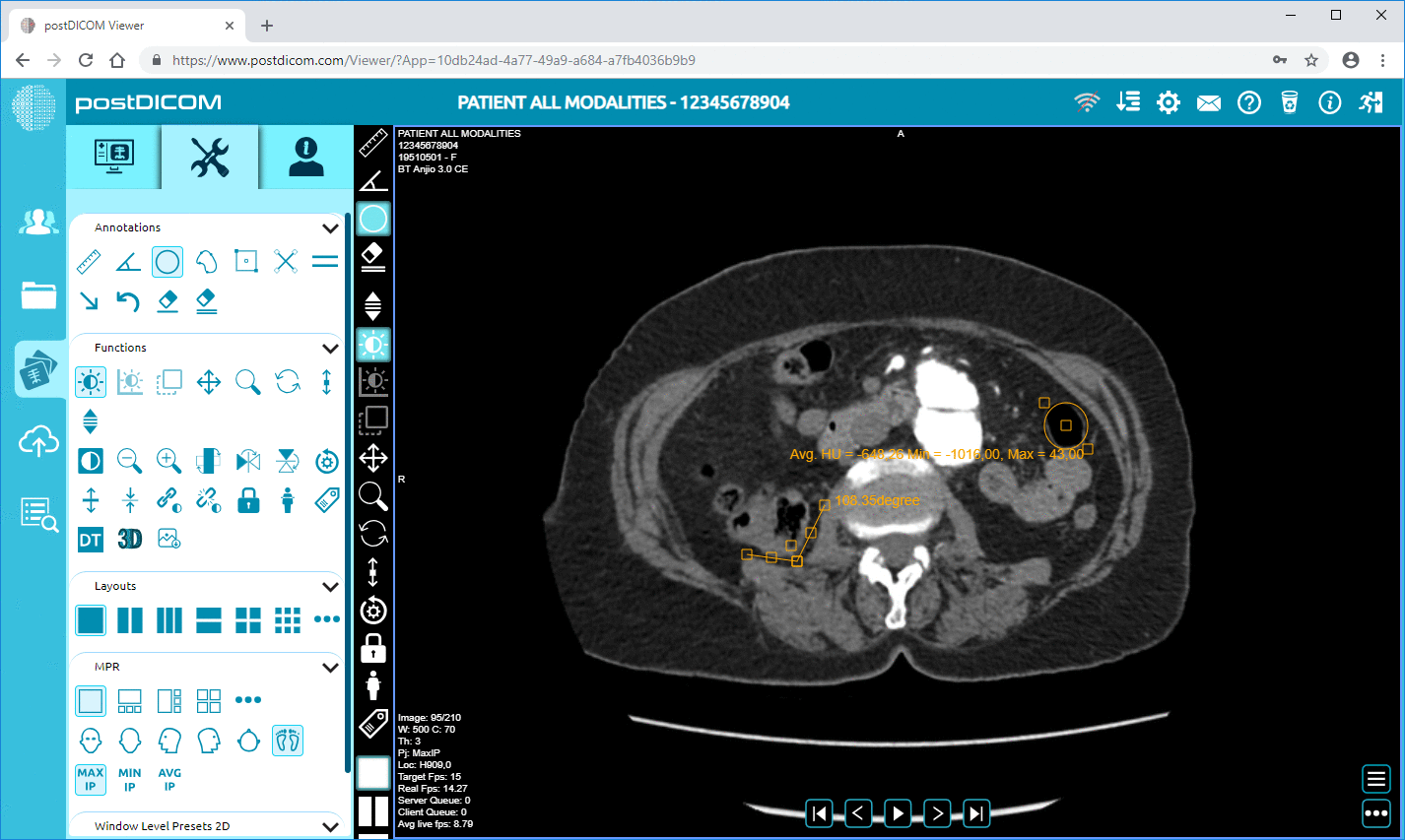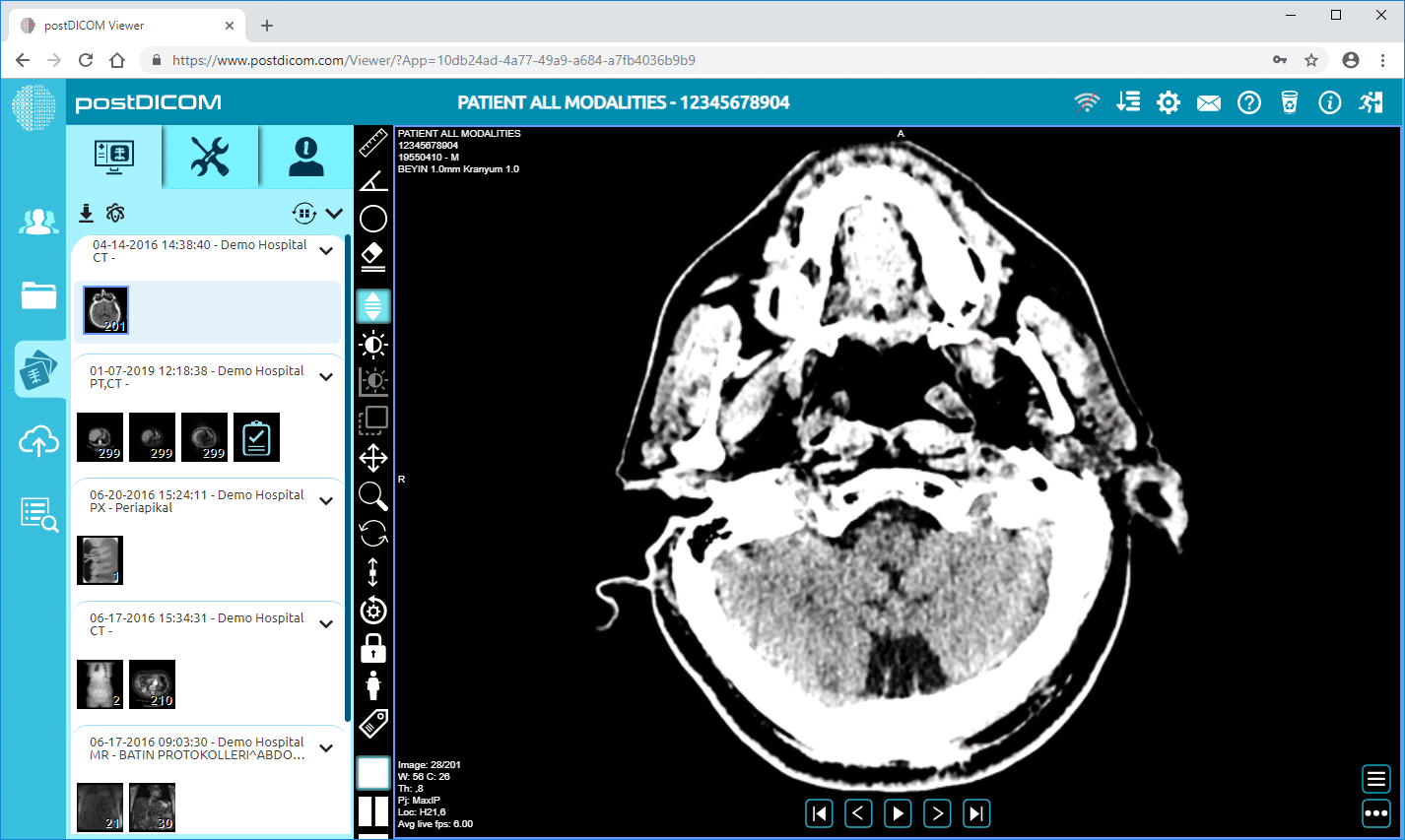
Cloud PACS and Online DICOM ViewerUpload DICOM images and clinical documents to PostDICOM servers. Store, view, collaborate, and share your medical imaging files. |