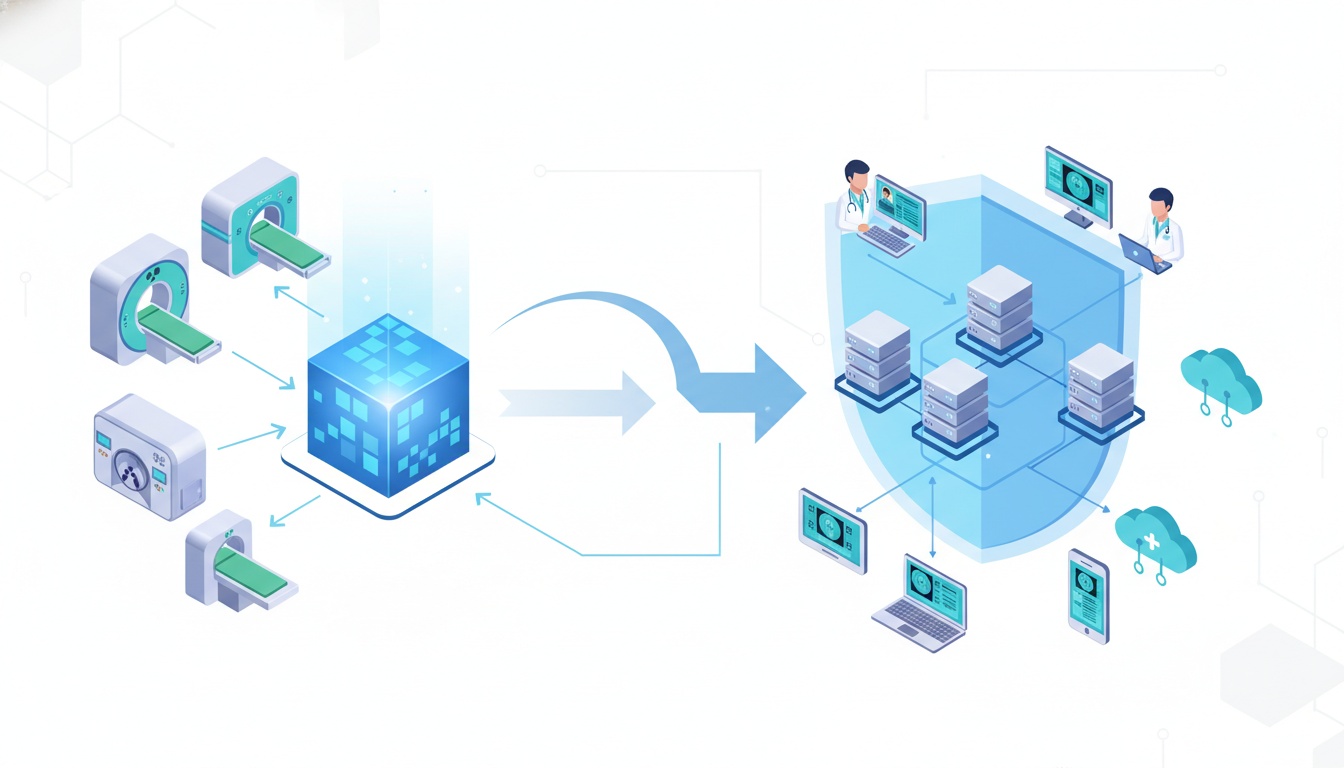
As medical professionals strive to deliver the best possible care, two technologies often take center stage: DICOM (Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine) and PACS (Picture Archiving and Communication System).
While often seen as competing forces, understanding their symbiotic relationship can unlock unprecedented levels of streamlining and optimization in your healthcare facility.
At PostDICOM, we've spent years immersed in the intricacies of these technologies. We know firsthand how DICOM, as the universal language of medical imaging, and PACS, the powerful storage and retrieval system, can work together to revolutionize your workflow.
This blog post will help you look beyond the surface-level differences between DICOM and PACS. We'll explore how their integration can enhance patient care, improve diagnostic accuracy, and drive operational efficiency.
Whether you're a hospital administrator, a radiology department head, or a healthcare IT professional, we will provide valuable insights to make informed decisions that benefit your facility and, most importantly, your patients.
DICOM and PACS are complementary. DICOM provides the standardization necessary for PACS systems to operate effectively across different devices and systems within the healthcare industry.
Scope: DICOM is a standard that defines how images and associated data should be handled, stored, and transmitted. PACS, on the other hand, is a system that implements these standards (among others) to provide practical solutions for the storage and access of medical imaging.
Functionality: DICOM facilitates interoperability between imaging systems and devices by standardizing image formats and communication protocols. PACS uses these standards to provide a full-fledged operational system that effectively helps healthcare facilities manage their imaging needs.
Dependency: PACS systems rely on DICOM standards to function correctly. Without DICOM, PACS systems could not ensure compatibility and interoperability among diverse medical imaging equipment and systems.
DICOM is a standard protocol for storing, transmitting, and managing medical imaging information and related data. It defines the formats for medical images that can be exchanged between devices and systems, ensuring interoperability among different systems and devices used in healthcare.
DICOM's main purpose is to ensure that medical imaging information is available in a standardized format that can be securely shared and used across various systems, regardless of the manufacturer. This facilitates the integration of medical imaging into broader healthcare workflows and systems.
Standardization: DICOM standardizes the image file formats and network communications to support a wide range of imaging applications, such as radiology, cardiology, and dentistry.
Metadata: Along with the image data, DICOM files include a header containing key metadata about the patient, the type of scan, image dimensions, and other diagnostic information essential for clinical use.
PACS is a medical imaging technology that provides economical storage and convenient access to images from multiple modalities. Essentially, PACS is a combination of hardware and software dedicated to storing, retrieving, distributing, and presenting images.
The primary purpose of PACS is to streamline the process of storing and accessing medical images and to replace traditional film-based methods, reducing physical storage and enabling easier and faster access to images.
Image Archiving: PACS systems provide a repository for imaging data that is both scalable and secure.
Communication: These systems enable the electronic distribution of digital imaging results (such as X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs) across users and departments within healthcare facilities.
Integration: PACS often integrate with other healthcare systems, including Electronic Health Records (EHRs) and Radiology Information Systems (RIS), enhancing workflow efficiency and data cohesion.
DICOM (Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine) ensures interoperability between different imaging devices through standardized protocols covering data formats, communication protocols, and network services.
This standardization enables various medical imaging devices and systems—regardless of their manufacturer—to exchange information seamlessly. Here’s how DICOM achieves this:
DICOM specifies a uniform format for medical images and associated data, including detailed information on how images and their metadata should be structured.
Metadata in DICOM files contains a wide range of information, such as patient ID, image type, device specifications, dimensions, and clinical details of the procedure.
By standardizing this format, DICOM ensures that any compliant device or software can interpret and display the data correctly, irrespective of where or how the image was created.
DICOM defines a set of protocols for the network communication of medical imaging information.
These protocols govern how imaging data is transmitted across systems. For example, DICOM includes specifications for querying and retrieving images from remote servers, submitting imaging results to other systems, and even pushing images to portable media like CDs.
These communication protocols ensure that different systems can exchange data efficiently and reliably.
DICOM also includes standards for various network services essential for practical interoperability. These include:
Storage Services: Rules for storing images and documents on a server or cloud system.
Query/Retrieve Services: Allows systems to search for and request images from other systems based on specific criteria (such as patient ID or date of examination).
Print Services: Standards for sending images to printers in a format that ensures they are printed correctly.
Worklist Management: Integrates imaging systems with hospital information systems to manage and synchronize patient worklists across departments.
DICOM requires devices and software systems that claim DICOM compliance to provide a DICOM Conformance Statement.
This document details how the device or system implements DICOM standards, including which options and features are supported. This transparency allows healthcare providers to verify that their equipment will interoperate correctly before integration.
DICOM categorizes data and services into "object classes" and "service classes." Object classes describe data types (such as different kinds of images), while service classes describe what can be done with the data (such as storing or transmitting).
This modular approach allows for very flexible implementation options that cater to specific needs while maintaining the overall framework for interoperability.
 - Created by PostDICOM.jpg)
PACS (Picture Archiving and Communication System) significantly enhances the accuracy of diagnoses in medical imaging through various mechanisms. These include improved image quality, faster access to images and relevant patient data, enhanced collaboration among healthcare professionals, and advanced imaging tools that aid in more precise evaluations.
1. Higher Resolution Images: Modern PACS often support high-resolution images crucial for detailed examinations. Better image quality directly translates into more accurate diagnoses, as finer details are more discernible, aiding clinicians in detecting subtle abnormalities that might be missed with lower resolution.
2. Immediate Availability: PACS systems store images digitally in a centralized repository, making them immediately accessible to authorized users across the healthcare facility or even remotely. This quick access means doctors can review patient images during consultations or treatments in real time, allowing for timely and more informed decision-making.
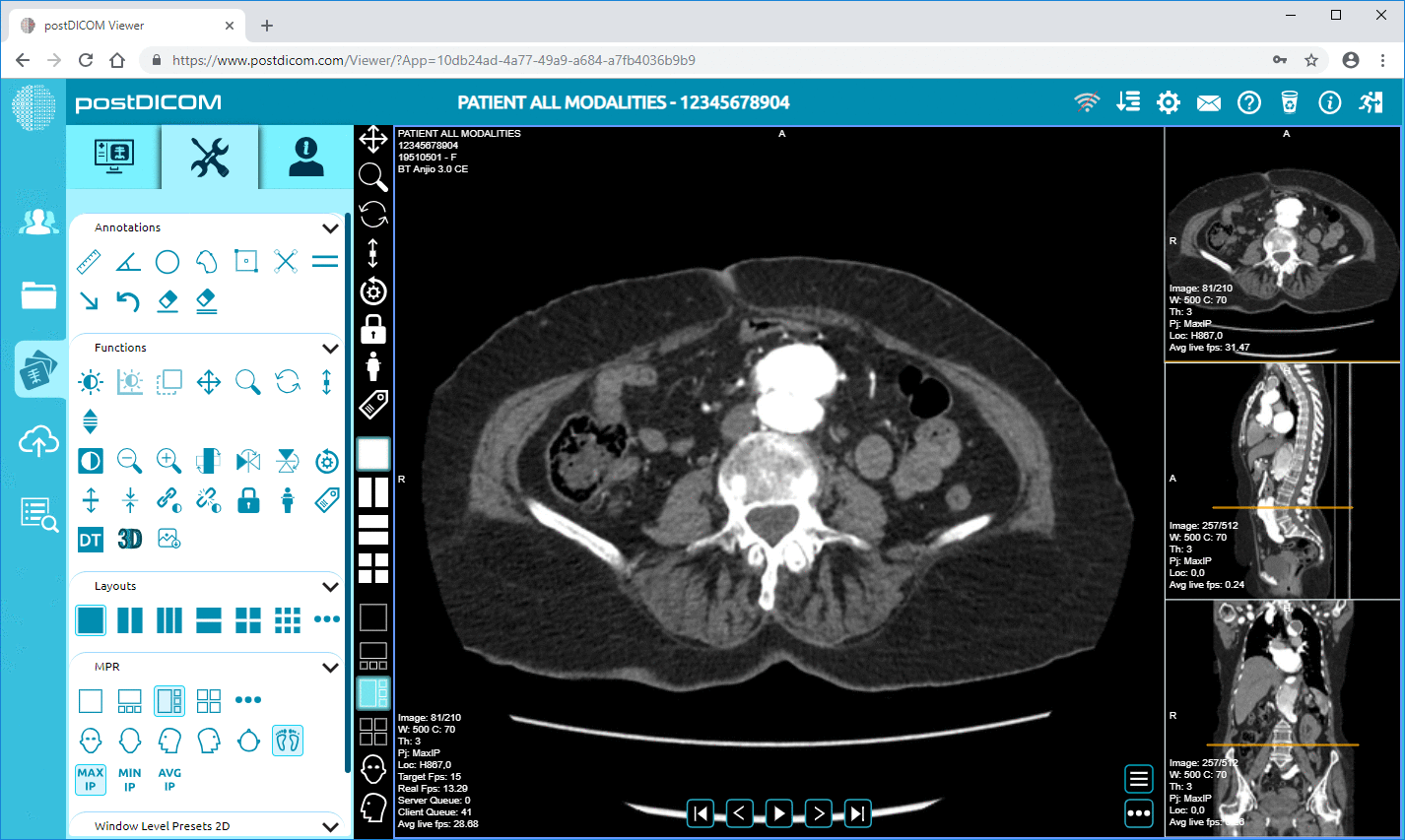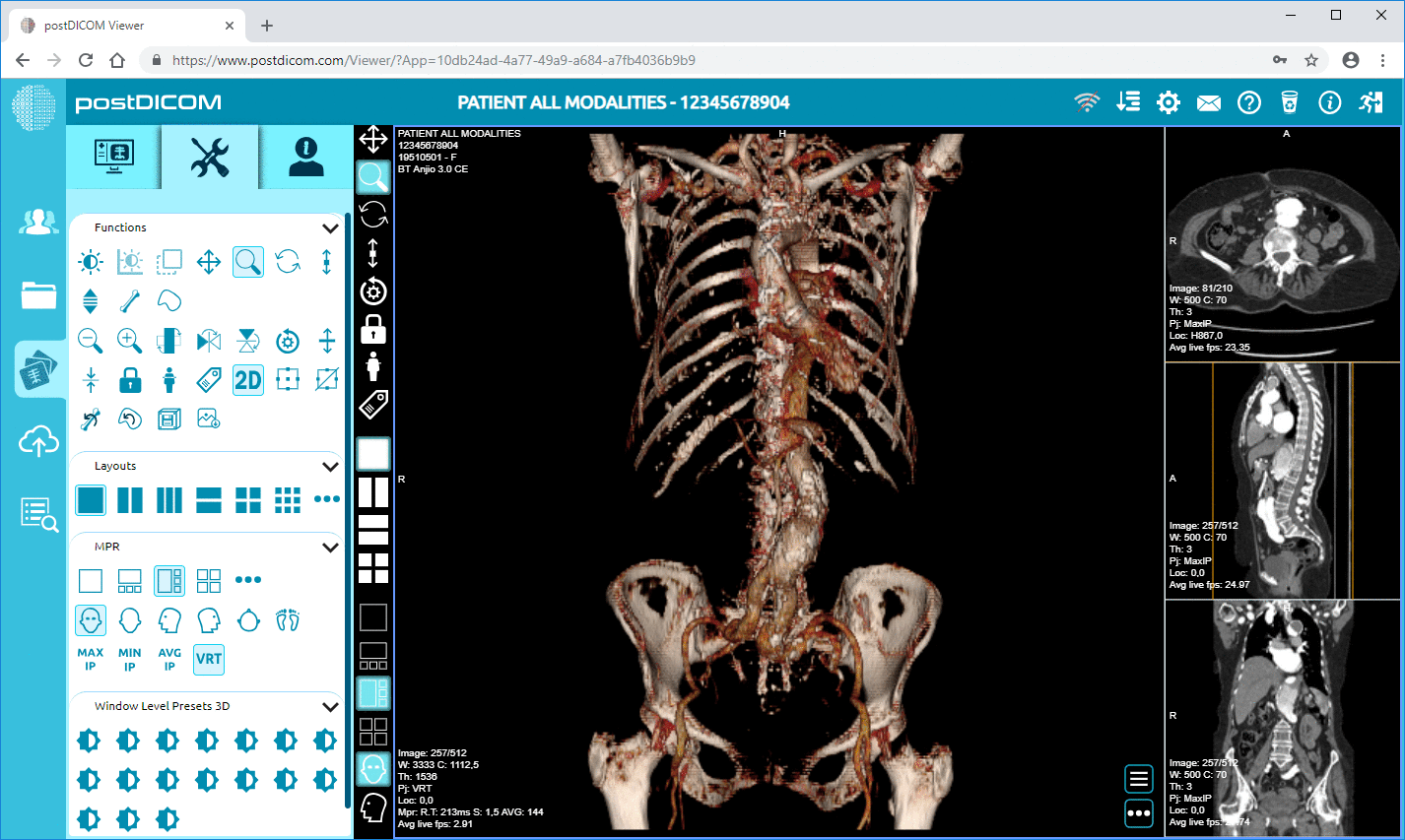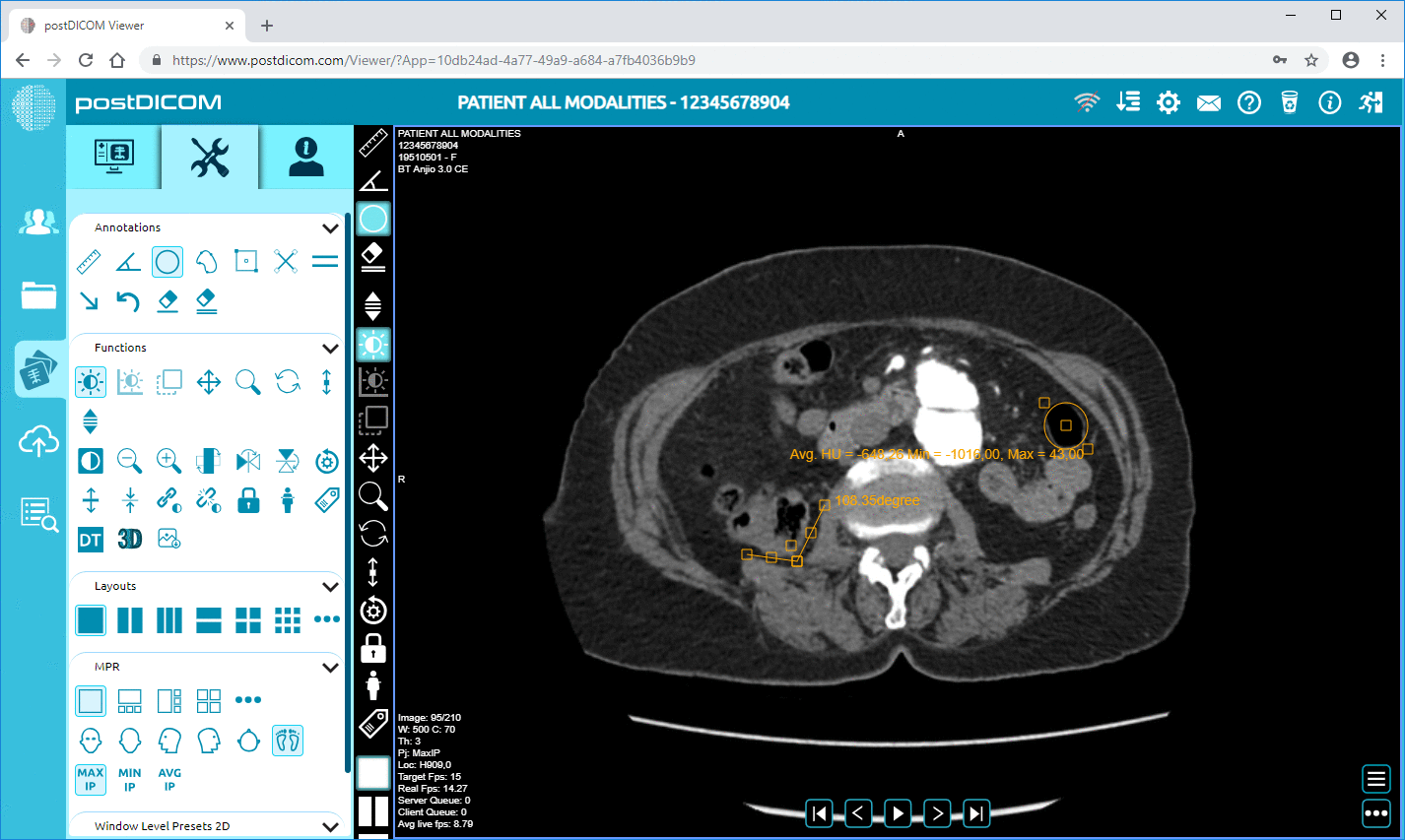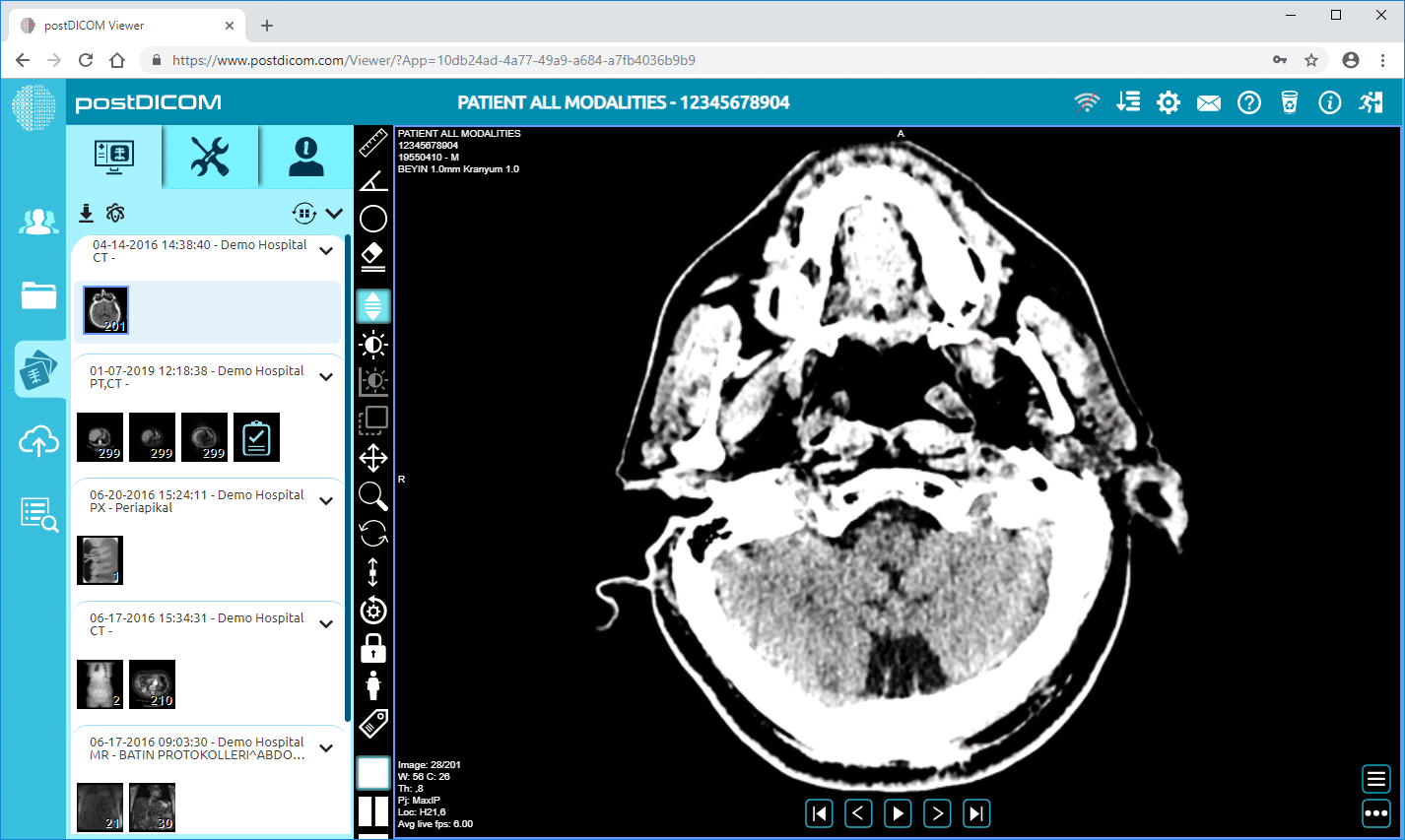
3. Enhanced Viewing Options: PACS provides various tools to enhance image viewing. These tools include zoom, rotate, measure, and to improve contrast features, which allow radiologists and other specialists to analyze images more thoroughly and accurately.
4. 3D Reconstruction: Some PACS offer advanced functionalities like 3D imaging, which can reconstruct two-dimensional images into three-dimensional models. This is particularly useful in complex cases involving structures that are difficult to visualize in 2D, such as intricate vascular anomalies or skeletal pathologies.
5. Integration with Other Systems: PACS is often integrated with other healthcare information systems such as Electronic Health Records (EHR) and Radiology Information Systems (RIS). This integration ensures that all relevant patient information, including past images, medical history, laboratory results, and pathology reports, is easily accessible. Having comprehensive patient information in one place helps clinicians make more accurate diagnoses by considering all aspects of a patient’s health condition.
6. Facilitating Second Opinions: With PACS, images can be easily shared with other specialists for second opinions without requiring the physical transport of films. This speeds up the consultation process and ensures that diagnoses are more accurate and less subjective as multiple experts review them.
7. Telemedicine Support: PACS supports telemedicine initiatives by allowing experts across different locations to access and review images. This is particularly beneficial for facilities in remote areas that may not have onsite specialists. Access to expert opinions ensures that patients receive accurate diagnoses regardless of location.
8. Audit Trails and Compliance: PACS maintains detailed logs of all interactions with the system, including who accessed which images and when. This feature is essential for compliance with healthcare regulations and for internal audits that help improve diagnostic procedures and training.
9. Quality Control Tools: Some PACS include quality control tools that automatically detect and flag image quality issues, such as underexposure or motion artifacts, which might otherwise lead to diagnostic errors.
The synergy between DICOM and PACS is undeniable. By understanding their unique roles and leveraging their combined strengths, your healthcare facility can unlock a new era of streamlined operations, improved patient care, and enhanced diagnostic accuracy. Remember, DICOM and PACS are not competitors but partners in pursuing medical excellence.
At PostDICOM, we are committed to empowering healthcare facilities like yours with the tools and expertise needed to harness the full potential of medical imaging technology. Our comprehensive suite of services, including PACS solutions, DICOM consultation, and integration support, are designed to optimize your workflow, enhance data security, and drive innovation in patient care.
Don't let the complexities of DICOM and PACS hold you back. Partner with PostDICOM and embark on a transformative journey towards a more efficient, effective, and patient-centric healthcare future. Contact us today to discover how we can tailor our solutions to meet your unique needs and elevate your medical imaging capabilities to new heights.
Together, let's redefine the possibilities of medical imaging and empower your healthcare facility to thrive in the digital age.
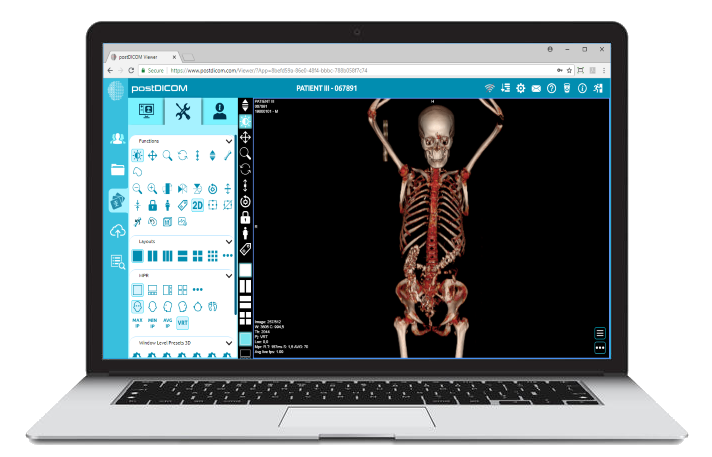
|
Cloud PACS and Online DICOM ViewerUpload DICOM images and clinical documents to PostDICOM servers. Store, view, collaborate, and share your medical imaging files. |